Epididymitis - Symptoms and Treatment
The testicles are the organ of the male reproductive system, in which the process of spermatogenesis is carried out( the formation of germ cells of spermatozoa with a haploid set of chromosomes).Maturation of mature spermatozoa occurs in the appendages of the testicles, which look like small, narrow tubes, also intended for the further movement of mature germ cells. The inflammatory process in the appendages is called epididymitis .It occurs in men quite often, mostly at the age of 20-40 years( there are cases of epididymitis in children).
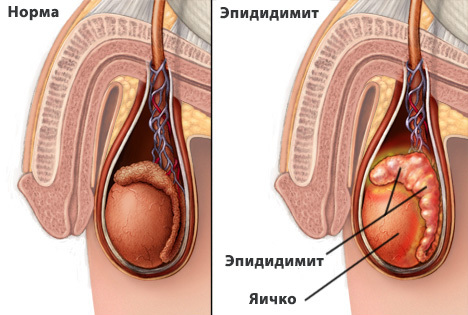
Fig.1 - Inflammation in the epididymis - epididymitis.
Content
- 1 in epididymis
- 2 mechanism of inflammation Causes
- 3
- 4 Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment
- 5 epididymitis
- 6 Consequences
- 7 Prevention
- 8 Can I have sex with epididymitis?
Mechanism of development of inflammation in the appendages of the testicles
The inflammatory process has a protective function. It develops with damage to cells and tissues of various locations. In this case, the cells of the immune system rush into the lesion, where various biologically active compounds start to be produced. The main mediators of the inflammatory reaction, which are produced by leukocytes, are prostaglandins. They are responsible for the mechanism of inflammation lead to swelling of tissues damaged area by increasing the permeability of the vessel wall( Blood plasma extends partially into the intercellular substance), irritating the sensitive nerve endings, and also reduce the outflow of the venous blood. Pain sensations in inflammation develop due to direct irritation of sensitive nerve endings with prostaglandins, as well as through mechanical compression during swelling of tissues. Biologically active compounds and inflammatory mediators increase the activity of leukocytes, which gradually eliminate the effect of the causative factor of inflammation.
Reasons for
There are several groups of causative factors that lead to damage to the cells of the epididymis, followed by the development of an inflammatory response. The main causes are infections caused by various microorganisms, which include:
- Nonspecific bacteria - cause the development of epididymitis most often. They do not have strict specificity for the tissues of the testicles, but if they get into them, they can cause damage to the cells. These bacteria include streptococci, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococci .Penetration Data pathogenic( disease-causing) microorganisms can occur in several ways - drift with blood or lymph from other foci of inflammation( hematogenous and lymphogenous route of infection), delivery directly by contact from nearby inflammatory focus in prostatitis( prostate inflammation), proctitis( direct pathologyGuts), orchitis( testicular damage).
- Genital Infections - some infectious diseases which are characterized primarily sexual transmission during prolonged chronic course can lead to an inflammatory lesion tissue of the epididymis( chlamydia, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea ).
- Viruses - exciter mumps( colloquially - pig) which belongs to the genus paramyxovirus, is tropic to glandular tissues and testes can infect cells and their appendages.
- Fungal infection - epididymitis may develop on the background of thrush( a fungal infection caused by fungi of Candida genus, which are conditionally pathogenic microflora) with a significant decrease in immunity activity.
Symptoms of
The development of epididymitis is accompanied by a number of clinical manifestations of the pathological process, the main of which are:
- The appearance of pain in the localization of inflammation - for this pathology is characterized by the fact that at the very beginning of the development of the pathological process, pain sensations can be localized mainly in the lower abdomen, as well as the lower back. This is due to the primary lesion of the vas deferens, after which the inflammatory process extends to the tissues of the epididymis. Then during the day, discomfort and unpleasant sensations are shifted directly into the scrotum. Severity of pain may be stronger on the one hand, which is associated with asymmetric inflammation( pathology has a more severe course on the right or left side).With a one-sided epididymitis pain sensations arise only from the side of inflammation.
- Pain in testicles - have a reactive character.
- Scrotal edema - characterized by a symmetrical or asymmetric increase in volume.
- Dysuria - the appearance of discomfort during urination in the form of pain or burning.
- Appearance of pathological impurities in urine and semen( more often in semen) in the form of veins of mucus, pus or blood, which depends on the cause of epididymitis.
Epididymitis can often be accompanied by common intoxication phenomena, such as a rise in body temperature( sometimes up to significant digits), weakness, decreased appetite, and aching muscles and joints.
Acute acute and chronic epididymitis are distinguished by the duration of the course. The acute course of the pathological process is characterized by a duration of up to 1 month, its cause is often a nonspecific bacterial, viral infection, a recent trauma. Symptoms of pathology have a pronounced intensity, the inflammation is mostly one-sided. Chronic epididymitis has a course duration of more than six months, clinical symptoms are not clearly expressed. The causes of this current are fungal, sex infections, prolonged intoxication of the body of a man.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of this disease is carried out for reliable explanation of the cause of the inflammatory process, which is necessary for the selection of adequate treatment. It includes several research methods, which include:
- Laboratory tests, by which the identification and identification of an infectious agent of inflammation is carried out. For this, a semen analysis is used with PCR( polymerase chain reaction, which makes it possible to identify and determine the species belonging to the genetic material of microorganisms), bacteriological investigation( seeding of the material under study for special nutrient media), microscopy. In order to identify specific antibodies in the blood that are formed by the immune system to the pathogen in response to the development of the infectious process, ELISA is used( enzyme immunoassay).
- Spermogram - a study of sperm, which determines the main indicators of the functional state of the testes and their appendages( sperm volume, its organoleptic characteristics, the presence of leukocytes and erythrocytes, evaluation of the shape and motility of spermatozoa).
- Clinical blood test, which determines the criteria for the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
- Clinical analysis of urine - gives an idea of the severity of the pathological process in the structures of the urogenital tract of a man.
- Ultrasound examination of the testicles and their appendages, allowing to visualize their structure and gross pathological changes.
The doctor selects the specific methods of the study individually, which is determined by the clinical symptoms of the disease, as well as the capabilities of the laboratory and the diagnostic department of the medical clinic.
Treatment of epididymitis
Treatment of this disease is complex, it includes several therapeutic approaches, which include:
- Etiotropic therapy aimed at eliminating the effects of the causative factor that led to the inflammatory response. For this purpose, according to the diagnosed reasons can be used antibiotics ( at nonspecific bacterial infection apply antibacterials group semisynthetic penicillins, cephalosporins, and for sexual bacterial infection preferred macrolides and tetracyclines), antiviral means in mumps and antifungal medications in case of fungal infection. The duration of etiotropic therapy is determined by the severity of the course of the pathological process, as well as by subsequent control laboratory tests.
- Pathogenetic therapy is necessary to restore the normal functional activity of the testicular epididymis tissues. It involves the use of absorbable means to prevent formation of connective tissue adhesions preventing movement of spermatozoa, but also anti-inflammatory drugs that block prostaglandin activity of mediators of inflammation.
- Symptomatic therapy - includes the use of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce the severity of pain and discomfort. In the long
Treatment with folk remedies usually includes use of medicinal plants .The most effective in reducing the severity of inflammation in epididymitis considered St. John's wort, wild rose, juniper, nightshade, marsh calamus .Before using them, always consult a physician. Consequences
Prolonged lack of adequate treatment of the disease or improper use of drugs can lead to different consequences, most formidable of which is the development of male infertility. Nonspecific bacterial infection with prolonged course can cause the formation of an abscess( a limited cavity in the tissues of the epididymis, filled with pus).Chronic epididymitis can cause the development of an inflammatory process in the tissues of the testicles.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of the disease is aimed at preventing the penetration of infection in the tissues of the ovaries. Prevention of sexual infection includes having sex with one constant sexual partner or using condoms( barrier method of protection).To avoid infection of a nonspecific bacterial infection, it is important to adhere to the rules of intimate hygiene. Abandonment of bad habits will help to maintain the activity of immunity at the proper level, and also reduce the toxic effect on the structure of the reproductive system.
Can I have sex with epididymitis?
The possibility of having sex with epididymitis is determined by the severity of the course of the pathological process, as well as the cause of its development. The acute course of epididymitis requires functional rest for the appendages of the testicles, so the employment of sex should be excluded. This also applies to inflammation, which is a consequence of sexual infection( there is a high risk of infection of the sexual partner).With chronic epididymitis, it is possible to have sex, but only after consulting a doctor.
General Practitioner Krivoguz IM
Recommended for viewing: