Hematuria in men - causes and diagnosis
Hematuria is a symptom of a pathological condition in which blood or erythrocytes appear in the urine. At the same time, the number of the latter exceeds the permissible norms. It can occur in diseases and traumas of the system of urination( kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra), as well as in diseases of other organs and systems.
Short description of the mechanism
Primary urine formation occurs in multiple glomeruli of the kidneys, each of which is a capillary network enclosed in a capsule( Shumlyansky-Bowman capsule).The wall of the capillaries consists of three membranes:
- internal, consisting of a single layer of endothelial cells;
- external - one layer of large epithelial cells from the side of the glomerulus capsule;
- medium( basal membrane), which is a structure of three layers formed by special filamentous collagen-like proteins, glycoproteins and lipoproteins, between which there are pores of filtration.
Basal membrane is a kind of filter. Through its pores, water molecules, low-molecular proteins, slags, etc., freely flow into the capsule of Shumlyansky, which is the primary urine. However, the pore size is much smaller than the volume of the formed blood elements, so that only the erythrocytes can pass through the basal membrane into the urine. From the capsule, the primary urine enters the tubules, where water, macronutrients, microelements, chlorine, proteins, etc., re-enter the blood, that is, secondary urine enters the ureters, the bladder and then into the urethra( urethra).
Diagnosis of hematuria
Hematuria, depending on the amount of blood, is divided into:
- Macrogematuria, manifested by staining the urine with blood and even the presence of blood clots in it.
- Microhematuria - visually urine has a normal color, but in laboratory research the amount of red blood cells in it exceeds the norm.
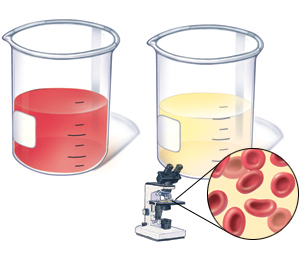
Fig.1 - Macrogematuria( red color of urine), microhematuria( usual color of urine).
With macrohematuria, it is possible to carry out a three-glass sample. For this, the patient is encouraged to simultaneously collect urine at the beginning, middle and end of urination, respectively, in 3 different containers. Depending on the intensity of urine staining in the portions, machemuturia are distinguished:
- Initial, in which the urine is maximally colored in the first container, which is a sign of a disease or trauma to the urethra.
- Terminal - the urine is most intensively colored in the third tank. Her expulsion is due to the contraction of the muscle of the bladder, as a result of which the altered mucosa is displaced and her vessels are injured. This is typical for diseases( usually inflammatory) of the neck of the bladder and the posterior urethra located in the neck wall.
- Total - the intensity of coloring the blood of all three portions of urine is the same. This type of hematuria is most common( inflammation of the bladder, kidneys, their traumatic damage, bleeding polyp of the bladder or urethra, malignant tumor, kidney stone disease).
In the urine, blood clots can also be detected. According to their form, it is possible to judge the source of bleeding: vermicular clots form in the ureters, and formless and large - in the bladder.
In microhematuria, the main diagnostic criteria are the laboratory quantitative determination of erythrocytes in the urine under a microscope. For this, 3 methods are used:
- counting in 1 ml of urine - men should normally not have more than 3 erythrocytes in each field of vision;
- counting in 1 ml urine sediment by the Nechiporenko method( normal in men - not more than 1,000).
- counting in 1 ml of urine sediment by the Addis-Kakovskiy method( the norm in men is no more than 1х105).
For the Nechiporenko method, the patient takes 50-100 ml of the average urine sample. Her fence is performed in the morning( preferably) or 3 hours after abstinence from urination. The urine is mixed, poured into a test tube of about 5 ml and centrifuged. The liquid part is drained, and 1 ml is taken from the formed sediment, in which the erythrocytes are counted under the microscope.
The Addis Kakowski study is carried out in the same way, but it is more informative, since urine is collected within 1 day or, if it is difficult for the patient, 12 hours. This method is especially useful for diagnosing intermittent( intermittent) form of hematuria.
Causes of hematuria
It is a nonspecific symptom of many pathological processes. The most common are:
- Acute and chronic infection of the urinary tract - acute cystitis, urethritis, acute or chronic pyelonephritis.
- Prostatic hyperplasia, acute and chronic prostatitis, prostate cancer.
- Renal stone disease, bladder or urethral polyps, bladder cancer, tumors and renal tuberculosis.
- Contusions of the kidneys and bladder trauma( when it is filled) with a fall or as a result of direct physical impact.
- Acute or chronic glomerulonephritis, diabetic angiopathy, connective tissue diseases of autoimmune etiology( systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatism, systemic scleroderma), systemic vasculitis( nodular periarteritis, Schönlein-Henoch disease).
- Thrombohemorrhagic syndrome, high blood pressure.
- Exposure to toxic substances and certain medications( aspirin, gentamicin, sulfonamides, etc.).
Different kinds of visual assessment and laboratory tests allow to determine the presence of the hematuria itself, to make a preliminary conclusion about its source, sometimes about the nature of the pathological process, and also to draw up a plan for further examination and treatment.
Recommended for viewing: